RL
SCIENCE | 9D
In this article you will find:
-
Ecology
-
Chemistry
-
Chemistry safety
-
Space
-
Physics
Am I missing something?
Give me a heads up if i'm missing something, curriculums change, science changes. If there needs to be something added give me a shout.

ECOLOGY
Ecology is the study of the interactions of the living things with each other and with the non-living factors in their environment. An ecosystem is an area where there is a particular set of relationships between the biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. Biotic factors are the living or once living components in an ecosystem and examples include animals, plants, bacteria, dead leaves etc. Abiotic factors are the non-living components in an ecosystem and examples include soil, rock, air, water, sunlight, temperature, etc. Ecosystems are made up of communities, which are a collection of all the populations’ of species.
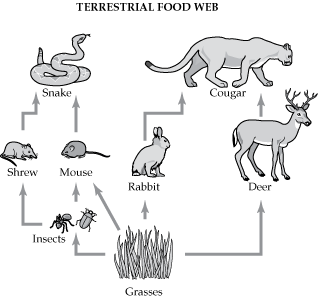
FOOD CHAINS AND FOOD WEBS
Producers vs. consumers vs. decomposers
There are 3 types of feeders on the planet.
Producers: green plants that make their own food inside themselves. Green plants do this using sunlight, carbon dioxide & water (Photosynthesis).
Consumers: need to eat other organisms. Animals (humans) and some plants do this.
Decomposers: Bacteria, fungus, and some insects are decomposers
Food Chain- a food chain is the series of organisms showing feeding relationships. A food chain almost always begins with a green plant (producer) which is eaten by an animal (consumer). The arrow means "is eaten by" and shows the flow of energy along the food chain. There are no decomposers in a food chain because there are so widespread and are not specific to just one food chain.
**Example of a food chain:
Grass -----> Grasshopper -------> Kookaburra
(Producer) (1st order consumer) (2nd order consumer)
First order consumer (also called the primary consumer) - the organism that eats the producer
Second order consumer (also called the secondary consumer) - the organism that eats it derives nutrients from the 1st order consumer
Herbivore - 1st order consumer eats vegetation
Carnivore- an organism that obtains nutrients from an Organisms blood or flesh
Omnivore- an organism which eats both plants and animals.
Scavenger- a consumer that eats dead animals
Decomposer - an organism such as bacteria or fungi that breaks down dead organisms and their wastes
Trophic Level - a trophic level is each level in a food chain. Water and energy are always lost as in urine, faces and heat energy at each trophic level.
Food web - a picture of interrelated food chains in a given area
ECOLOGY
ENERGY IN ECOSYSTEMS
The source of all energy for an ecosystem comes from the sun. Much of the suns radiant is filtered out by molecules in our atmosphere. Radiant energy is energy that travels through space
*only 0.023% of the suns energy is used for photosynthesis
ENERGY TRANSFER WITHIN TROPHIC LEVELS
Trophic level - a method to categorize lining organisms according to how they gain their energy (what they eat)
Autotrophs (1st trophic level) -self feeders, produce their own food
Heterotrophs (upper trophic levels) - Cannot produce own food, need to consume other organism for energy (consumers)
-> Energy is transferred between each trophic level. Only 10% is transferred from one trophic level to the other.
-> During each energy transfer more energy is lost
-> This is lost through heat and incomplete digestion
-> The organism that is being consumed uses some of the energy to live out its life
-> Because of the loss of energy from one trophic level to the next, there can only be five trophic levels in a food chain.
NITROGEN CYCLE
The series of processes that moves nitrogen compounds (nitrites (NO2-), nitrates (NO3-) and nitrogen gas (N2)), throughout the lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere.
Losses: assimilation (incorporation of nitrogen into biomass) dentrification (bacteria breaking nitrates -> N2
Gains: nitrogen fixation (bacteria capable of turning nitrogen gas into nitrates decomposition/ammonification, nitrification
Man’s interference: fertilizers runoff into waters, eutrophication, sewage > ammonification, burning fossil fuels, oxides of nitrogen + H2O in air, Nitric + Nitrous acid, Acid rain
CYCLES OF MATTER
Nutrients that organisms need are continuously cycled between the abiotic environment and the living organisms through biogeochemical cycles (nutrient cycles) that include Hydrologic (water), carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorous
WATER CYCLE
The water cycle is the series of processes that moves water through the environment
Losses: evaporation, transpiration, run off
Gains: precipitation, condensation, percolation, ground water (96% of FW comes from here)
Man's interference: using groundwater faster that replaced, deforestation, pollution, building dams for generating electricity factories + industrial development.
CARBON CYCLE
The carbon cycle is the series of processes that moves carbon compounds throughout the lithosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are processes in the carbon cycle.
PHOTOSYNTISIS
Plants are producers. They are called this because they produce their own food for energy through the process called photosynthesis. Chlorophyll in plants into glucose (sugar) and oxygen.
Carbon dioxide + water + light energy + glucose + oxygen
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
=> Mitochondria
All animals consume food and used with oxygen to produce energy. This process is called cellular respiration. This is different from breathing cell Carbon Cycle. (Opposite of photosynthesis)
Losses: photosynthesis, diffusion into water
Gains: respiration, sombustion of fossil fuels, diffusion
Man’s interference: increase in fossil fuel consumption, factories + industrial development, deforestation, climate change
TERRESTRIAL CANADIAN BIOMES
Tundra:
Abiotic factors:
-Very cold winters, cool short summers
- Very little precipitation (mainly snow), permafrost
-Windy
Biotic factors:
-Lichens, mosses & dwarf shrubs
-Polar bears, arctic fox, muskox, lemmings, ptarmigan
Boreal Forest:
Abiotic factors:
-Cold winters, cool summers
-Lots of precipitation
-Acidic soil
Biotic factors
-Lichens, coniferous trees, peat moss
-Moose, bears, wolves, hawks, mosquitoes
Temperate deciduous forest:
Abiotic factors:
-Cool winters, warm summers
-Lots of precipitation
-Fertile soil
-4 well defined seasons
Biotic factors
-Deciduous trees, shrubs, grasses, flowering plants
-Deer, songbirds, rabbits, bears, raccoons
Temperate Grassland:
Abiotic factors:
-Cold winters, hot summers
-Moderate precipitation
-Rich fertile soil
Biotic factors:
-Grasses, some flowering plants
-Bison, hawks, snakes, pronghorns, voles, prairie dogs
Temperate Rainforest:
Abiotic factors:
-Warm damp summers, mild wet winters
-Humid, lots of precipitation
-Nutrient poor soil
Biotic factors:
-Douglas fir, western red cedar, deciduous trees that keep their leaves
-Bears, lynx, coyotes, vultures
Mountains:
Abiotic factors:
-Changes with altitude, base of mountain like temperate deciduous forest, top of mountain like tundra
Biotic factors:
-Small coniferous trees then alpine flowing plants, then mosses & lichens
-Bears, wolves, squirrels, sheep, goats
* The main four biomes in Canada are tundra, boreal forest, temperate deciduous forest and temperate grassland
EARTHS FOUR SPHERES
1) biosphere- the zone in or around the earth where life exists
2) atmosphere- the layer of gas that surrounds the planet
3) lithosphere- rocky outer shell of the earth/ the crust (soil)
4) hydrosphere- the water above on or below the Earth’s surface.

CHEMISTRY




Pictures of wildlife and nature
(Feel free to use these in a project!)
CHEM SAFETY & INTRO
TERMS
Hypothesis: an educated guess or prediction of the answer to the problem.
Data: results of an experiments, may be recorded in tables and graphs, diagrams or written words.
Variables: factors in experiments
Independent: the factors in an experiment that the investigation can manipulate (You can change)
Dependent: the factors in an experiment that the investigator cannot manipulate but this factor may be affected by the independent variable (You can’t change)
Control: the set up in an experiment that is used for comparison
Observations: what you make during an experiment using your 5 senses
Qualitative: physical descriptions of something (shape, colour, texture, odor, taste)
QuaNtitive: measurements that involve numbers (mass, length, volume, temperature)
Black box: something that can only be studied using indirect observations
Direct: observations that are made first hand using your 5 senses
Indirect: observations that you infer because you do not observe
Model: a mental image of something
-> 4 types 1) hard description 3) diagram
2) actual physical model 4) ineligible word
Theory: a list of assumptions based on observations that are used to explain something
Controlled experiment: an experiment where the independent variable is purposely changed to find out what change, if any occurs in the dependent variable.
Observation study: the careful watching and recording of a subject or event to gather scientific information (data) to answer a question.
SCIENTIFIC PROCEDURE
-
Identifying the problem question
-
Going to the library or go on the internet to find an answer to your problem.
-
Predict an answer to problem. (Hypothesis)
-
Designing the experiment (procedure)
-
Collecting the apparatus/equipment
-
Assembling the apparatus
-
Carrying out the experiment
-
Making observations. -5 Senses (sight, touch, taste, scent, hearing)
-
Recording observations
-
Interpreting
-
Checking the results around the original prediction
-
Making conclusions
APARATUS:
-
Beaker tongs
-
Test tube holder
-
Thistle funnel
-
Test tube brush
-
Tweezers
-
Glass plate
-
Test tube rack
-
Crucible & lid
-
Deflagrating spoon
-
Crucible tongs
-
Beaker
-
Utility clamp
-
Retort stand
-
Funnel
-
Medicine dropper
-
Watch glass
-
Scoopulas
-
Gas bottle
-
Erlenmeyer flask
-
Bunsen burner
-
Stoppers
-
Graduated cylinder
-
Ring clamp
-
Gas lighter
-
Wire gauze
-
Evaporating dish
-
Florence flask
-
Mortar & pestle
-
Stirring rod
-
Clay triangle
-
Test tube
-
Tongs
CHEMISTRY
MATTER
=>is everything in the universe
=>composed of three states - phases
Particle Theory:
When we observe matter, we see that is behaves in countless ways and can be put to countless uses. But is matter one definable thing? Over the Centuries, scientists have created many models to explain what matter is, to explain what lies beyond what we can physically observe. One of the most enduring models of matter is particle theory
1. Matter is made up of tiny objects, also known as particles
-
All particles of one substance are the same. Different substances are made of different particles
-
The space between the particles are large compared to the sizes of the particles themselves
4. The particles are always in motion/ vibrating. The more energy the particles have, the faster they move
5. There are attractive forces between the particles. The closer the particles the stronger the attraction
Three States of matter

CLASIFICATION OF MATTER
Pure substance- something that contains only one type of particle. They are all the same. Element and compounds are pure substances.
-
consists of only one kind of atom
-
is made up of 2 or more different atoms that are CHEMICALLY bonded (atoms=Elements)
-
is made up of several (2 or more) different pure substances
Heterogeneous Mixture- (mechanical mixture) A mixture where 2 or more substances can be seen or felt. (e.g. Bowl of cereal)
Homogeneous Mixture- (solution/ alloy) A mixture that looks and feels like it is made of only one substance. (e.g. Bottle of pop)
**Heterogeneous mixtures tend to be opaque, however homogenous mixtures tend to be transparent or clear
Physical properties- is a characteristic or description of a substance that may help to identify it
Chemical properties- describes the behavior of a substance as it becomes a new substance
Physical change- the substance remains the same but the form or state may change
Chemical change- the original substance is changed into one of more different substances. The new substance will have different properties form the original substance

THE ATOM & SUBATOMIC PARTICLES
The Atom is the smallest unit of an element that displays the properties of that element.
Each and every atom is made of 3 things:
-
Protons, positively charged particles, P+
-
Neutrons, neutrally charged particles, N°
-
Electrons, negatively charged particles, E-
The center of an atom is called the nucleus. Located inside the nucleus are the protons and neutrons. (These are the heavier particles of the 3)
The electrons in an atom are found travelling around the nucleus in energy levels
STANDARD ATOMIC NOTATION
The standard atomic notation is a communication method used by scientists.
P+=equal to Atomic Number
E-=equal to Atomic Number
N°=Atomic mass – Atomic number (then round)

This is an example of atomic notation. (For Sulpher)
On a typical periodic table, atomic mass # is on the bottom and atomic # is on the top. Simply reverse this to do standard atomic notation
DRAWING A BOHR-RUTHERFORD DIAGRAM
-
Determine the number of heavy particles (protons + neutrons) in the nucleus of the atom.
-
The number of protons and electrons are the same as the atomic # of the atom.
-
N°=Mass number – Atomic number
-
Draw a circle of a nucleus
-
Place the correct # of protons and neutrons inside the nucleus. (use the symbols after)
-
Draw another circle for the first energy level. Only 2 electrons can be in this energy level, they must be paired together
-
Draw another circle for the second energy level. Only 8 electrons can be places in this energy level and they must be paired. Place one electron in the 12, 3, 6, 9 o’clock positions. Then pair each electron up in the same way.
-
The third and fourth energy levels can only hold 8 electrons each.

This is an example of a Bohr-Rutherford diagram. (For Potassium)
Notice how the electrons are not on the nucleus. DO NOT MAKE THIS MISTAKE. Your first energy level is different from your nucleus.
DRAWING A LEWIS DOT DIAGRAM
This type of diagram shows the valence electrons (outer energy level electrons)
-
Draw the symbol of the atom
-
Using circles or “o” to represent the valence electrons
-
Place the correct # of valence electrons around the atomic symbol the same way as to fill a Bohr-Rutherford Diagram energy level

This is a Lewis dot diagram for Lithium. ONLY DRAW IN THE VALENCE ELECTRONS
THE PERIODIC TABLE
There are 90 naturally occurring element son this planet and even more are synthetically made in a lab.
How can these elements be organized?
Dimitri Mandeleev was a Russian Scientist who first discovered the trends of the elements.
Scientists later placed the elements in columns (families) and rows (periods)
The families represent the number of electrons in the outer shell. (Valence) These electrons help determine many properties
The periods represent the number of energy levels that contain electrons
The elements are organized according to their atomic number and atomic structure.
There are 3 types of elements: Metals, Non-metals, and Metalloids.


Malleability – ability to be bent or hammered without breaking
Ductility – ability to be stretched into wire without snapping
Metalloids- Share properties of both metals and non-metals
ORGANIZATION OF THE PERIODIC TABLE
-
Each horizontal (left to right) row is called a period
-
Each period represents a new energy level for electrons
-
As you move from left to right in a period, the valence outer energy level fills up with electrons
-
Each vertical (up and down) column is called a family or group
-
Each group contains many elements with similar properties (because they all have the same # of valence electrons
COMMON GROUPS OR FAMILIES
Alkali metals family-
-
First column (Li, Na, K, Rb, Fr)
-
Does not include HYDROGEN (properties do not match)
-
All have one valence electron ( that they lose)
-
All shiny, lightweight, reactive metals
Alkaline Earth family-
-
Second column for the left (Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra)
-
All have two valence electrons (that they loose)
-
Very reactive, but not as much as alkali metals
Noble gasses family-
-
Far right column (He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn)
-
All have a full valence
-
Are unreactive (very rare that they react with anything)
Halogens-
-
Second column from the right (F, Cl, Br, I, At)
-
All have 7 valence electrons (needs 1 more to become full valence)
-
Very unreactive, especially with metals that lose an electron to fill the valence energy level
-
They are all POISONOUS
Tip: don’t get frickle-fracked up with halogen gas. Not cool.
CONCLUSIONS
-
The non-metals like to gain electrons to fill the valence. (Outer energy level)
-
The metals like to lose electrons to empty the valence. (Outer energy level)
MOLECULAR COVALENT COMPOUNDS
Covalent (Molecular) Bond- A bond where two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons between them. The shared pairs are attracted to the nuclei (protons) of both atoms.
Molecule- Two or more atoms joined together by molecular bonds
Molecular compounds- Can be solid, liquid or gases at room temperature. They are usually good insulators but poor conductors of electricity. They have relatively low boiling points.
A compound that contains only non-metal elements in a combination of two are more different types of atoms
MONATOMIC IONIC COMPOUNDS
Monatomic ions are ions that consist of only one atom
How to write formulas for monatomic ion compounds:
-
Write the symbols of the cation first then the anion
-
Criss-cross rule: write the ionic charges above the symbols and criss-cross then to make them subscripts.
This is the equation for calcium bromide. See that you switch the charges. Note: Calcium is not Ca1 . Anything with one charge stays the symbol.

IONIC COMPOUNDS
-
A compound that contains 1 metal and at least one non-metal
-
Have high melting points
-
Form crystals, which form a regular repeating pattern of particles
-
Dissolve in water to form a solution that conducts electricity
-
Are solids at room temperature
IONIC BONDING
-
A bond between a metal and a non-metal
-
A bond where there is a transfer of electrons
-
An electrostatic attraction between a CATION (POSITIVE) ION and an ANION (NEGATIVE) ION
REPRESENTING IONIC COMPOUNDS
Combining Lewis dot diagrams for the elements we can represent ionic compounds as Lewis Structures

Sodium loses its valence electron because it is metal. Bromine gains the electron because it is non-metal. Formula is NaBr. The scientific name is Sodium Bromide
WHAT IS AN ION?
An ion is an atom that has lost (an) electron(s) (Metal atom) or gained (an) electron(s) (Non-metal)
The negative ion particle has a negative charge because it has more electrons that protons. (Anion=negatively charged)
The positive ion particle has a positive charge because there are less electrons that protons. (Cations=positively charger ion)
Metal atoms lose enough electrons to completely empty its outer energy level.
Non-metal atoms gain enough electrons to completely fill its outer energy level.
MOLECULES
A molecule can be both an element and a compound. A molecule contains 2 or more atoms that are the same or different. The group of 7 +1 is an easy way to remember the 8 elements that are diatomic. (Molecules) Nitrogen (N2) Oxygen (O2) Fluorine (F2) Chlorine (Cl2) Bromine (Br2) Iodine (I2) Astatine (At2) + Hydrogen (H2)
*A molecule cannot contain a METAL element
INTERPRETING CHEMICAL FORMULAS
-
Determine how many different elements are in the formula by their symbols
-
Determine how many atoms of each element are in the formula by checking the small number following the element symbol. (Note: if there is no number following the symbol, assume there is 1 atom)
-
Determine the total amount of atoms in the chemical formula by adding them up.
When an equation looks like this: 3(C2H4)
Multiply everything in the brackets by that outer number.
When an equation looks like this: Be(ClO4)2
Multiply everything in the brackets only by the LONE NUMBER outside the brackets.
NOMENCLATURE
Nomenclature is the naming of chemical compounds and molecules.
If the chemical formula is a MOLECULE (Only non-metals) then it will have the following rules applied to it: Use the suffix “–IDE” for the last element in the formula
Use Prefixes (Mono, Di, Tri, Tetra, Penta, Hexa…) For EVERY element in the formula depending on how many atoms there is per element. EXCEPTION TO THIS RULE: If the FIRST element in the formula has only one atom, DO NOT put “Mono” in front of it.
If the chemical formula is a COMPOUND (Metal + Non-metal mix) then it will have the following rules applied to it:
Use the suffix “-IDE” for the last element in the formula
ROMAN NUMERAL INTERPRETATION
If the name of the Chemical formula has a roman numeral in it, you are to interpret that as the charge of the element it follows. This is because not all elements have the same charges every time!
IDENTIFYING CHEMICALS
Water (Vapour) Cobalt blue paper turns a light pink colour from a blue colour.
Carbon dioxide turns limewater from clear and colourless solution to a milky cloudy colour.
Hydrogen when a burning splint is placed in the gas a pop sound (explosion) takes place
Oxygen When a glowing splint is placed in the gas the splint ignites

SPACE
WHATS IN THE SKY
The study of space and beyond the Earth is called astronomy. The universe is everything. A group of stars in the night sky is called a constellation. These objects have been used for years to help people navigate and record time
The solar system is made up of 8 planets (Plus three dwarf planets) and 1 star. Stars (in our solar system the sun) are objects that give off their own light – luminous. Planets are non-luminous – meaning light must reflect off them to be seen

GALAXIES
A galaxy is a huge collection of gas, dust and hundreds of billions of stars. These objects are attracted to each other through the force of gravity. There are 4 types of galaxies: spiral, elliptical, lenticular and irregular. Galaxies are moving further and further apart
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE
Expanding is a phenomenon that demonstrates that the universe is redshift.
The Big Bang Theory – If galaxies are moving further apart at some point in time they must have been closer. “Time zones” is when galaxies were next to each other. Time zero is estimated to be 10 million to 15 billion years ago. The event what the mass began to move apart is called big bang.
Nebula- is a spinning mass of gas and dust. All stars are born from nebulas. Gravity causes the matter of the nebula to spin. The dust in the centre becomes the stars and the rest if the dust forms the planets.
STARS AND CONSTELLATIONS
A constellation is a region of stars as viewed by Earth’s night sky. The Earth’s rotation makes it look like constellations are moving across the sky from west to east. The Earth’s revolution around the sun allows us to see different constellations with each passing season.
HOW A STAR IS BORN
-
A region of a nebula collapses on itself, gravity starts pulling gasses and dust together
-
The mass grows and begins to heat up, spinning, contracting, etc. forming a protostar
-
When the protostar heats up enough (million degrees Celsius) then the nuclear reactions take place
THE SUN
The Sun’s mass is roughly 1.99 x 1033 kg. This is about 333 000 times the mass of the Earth. The sun contains 99.8% of all of the mass in the solar system
THE INNER PLANETS
Known as terrestrial planets because they are small and rocky planets. (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars)
THE OUTER PLANETS
Known as the gas giants. They do not have a solid surface but have a small solid core of liquid or solid elements. (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune)
** Dwarf planet Pluto is no longer considered a planet.
MOONS
Objects that revolve around planets are called satellites. They can be natural or artificial.
ASTEROIDS
There is a section of our solar system between Mars and Jupiter called the asteroid belt. This area is a ring or thousands of small rocky objects called asteroids.
METEORS AND METEORITES
A meteor is a chunk of rock or metal that enters the Earth’s atmosphere from space and burns up due to friction. A meteorite is a meteor that doesn’t burn up all the way and hits the Earth’s surface. Meteorites can cause a lot of damage
COMETS
Composed of ice and dust travelling in a very long orbit around the sun. The closer the comet is to the sun, the larger its tail becomes. The actual comet is only a few kilometers wide, but the tail can be up to a million kilometers long.
THE MOTION OF PLANETS
The earth travels through the solar system in 2 different types of motion. Rotation is when the Earth rotates around its axis. It takes the earth 24 hours to do this. Polaris (The North Star) is in line with the Earth’s axis directly above the North Pole.
Revolution is the movement of one object around another. Planets revolve around stars. The Earth revolves around the sun in 365.24 days (One year)
SEASONS
Tilt of the Earth’s axis (23.5°) causes the seasons. But do all countries experience all 4 seasons? Countries near the Equator only experience 2 seasons wet and dry. Countries in the northern and southern hemispheres experience summer, winter, spring and autumn.
THE MOON AND ITS PHASES
How did the moon form? It is believed by scientists that the moon formed after a celestial object the size of mars collided with the Earth causing molten rock from the Earth to fly into space.
The moon takes 27 days to revolve around the earth. The moon also takes 27 days to spin on its axis. The Lunar Cycle begins with a new moon, then as more and more of the moon becomes visible until a full moon is present. This is called Waxing. Waning is when the moon changes back to a new moon.


PHYSICS
RULES OF ELECTRICITY
-
When voltage is increased the current also increases.
-
When the resistance is increased the current will decrease
-
In a series circuit, when the # of loads is increased (R increases) then the current decreases and the voltage across each load decreases but the sum of the loads voltage remains the same.
CIRCUIT SAFETY
Fuse/ circuit breakers
Do: opens the circuit when there is too much current.
Prevents: -> short circuiting-> wire from over-heating-> damage to electrons
Three pronged plug
Do: connects the device (load) to the ground wire of the houseprevents: -> electrocution-> protects the device
Ground Fault Circuit Interceptor (GFCI)
Do: opens the circuit when there is a change in current or when water is detected.
Prevents:-> water from damaging the circuit-> electrocution
ELECTRICAL GENERATION
There are 2 main components needed for the homes in Ontario to get electrical energy
1. The grid (the wires)
2. Generators (plants that make power)
1. A generator is a device that produces electricity by rotating a wire coil near a magnet
2. the electrical energy distribution grid is a network that carries electricity from the generation station to the consumerthe diagram below explains how electricity is produced and then transported to homes in Ontario
For a diagram of these please refer to page 476 of your academic grade 9 Science textbook.
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
Electric circuits are continuous paths where electrons flow. A circuit incudes an energy source, a load, conductors, and usually a switch
A load is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into another form of energy.

A switch is a control device that allows you to safely open or close a circuit.

An energy source is a device that provides electrical energy to the circuit. Examples are batteries or electrical outlets.



In order for the circuit to run the load, the circuit must be closed using a wire(s) (the pathway is all connected)
CIRCUIT SYMBOLS AND CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS
There are 2 types or circuits:
-
Series Circuits- A circuit with two or more loads that are connected one after the other so the electrons only follow one path
-
Parallel Circuits- A circuit with two or more loads that are connected so that the electrons can follow more than one path.
CURRENT (I)
The rate (how many) of flow of electrons. The unit to measure current is Amperes/ Amps (A). To measure current we use an ammeter
POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE/ VOLTAGE (V)
The difference in electrical potential energy. The unit to measure voltage is volt (V). To measure voltage we use a voltmeter.
ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE (R)
The ability of a material to oppose the flow of electrons through it. The unit to measure Resistance is the Ohm (Ω). To measure resistance we use an Ohmmeter.
CIRCUIT PROPERTIES
Series circuit
Voltage- Each load uses a portion of the voltage supplied by the battery
Current- The current is the same throughout a series circuit
Parallel circuit
Voltage- Each load uses all the voltage supplied by the battery
Current- The current is divided into different paths. The pathway with less resistance will have greater current.
RULES OF VOLTAGE AMPS AND RESISTANCE
-
When voltage is increased the current increases
-
When resistance is increased the current will decrease
-
In a series circuit when the number of loads is increased (R increased) then the voltage across each load decreases but the sum of the loads voltage remains the same.
ENERGY AND ELECTRICITY
There are 6 common forms of energy:
-
Chemical (e.g. fireworks)
-
Thermal (e.g. Heat production)
-
Sound (e.g. Voice)
-
Radiant (e.g. sun)
-
Mechanical (e.g. wind)
-
Electrical (e.g. lightning)
Electrical energy is a type of energy that comes from the flow of electrons
ENERGY TRANSFORMATIONS
Energy is interchangeable- meaning on type of energy can be changes into another.
ELECTRICAL CHRAGES
Electric force is the attraction or repulsion between charged objects.
The law of electric charges states:
Objects with opposite charge will attract each other and objects with like charges will repel each other. Objects can have a Positive charge or negative charge or have no charge (be neutral)
CAUSE
Electrons (negative charge) and protons (positive charge)
If an object has more electrons than protons then it will be negative
If an object has less electrons than protons it will be positive
If an object has equal amounts of electrons and protons then it will be neutral
HOW
Objects are made up of billions and billions of atoms. The electrons of some atoms can move from one atom to another. When they move they transfer electric charge. Protons cannot move between atoms. When atoms gain electrons, the neutral object becomes negatively charged. When atoms lose electrons, the neutral object becomes positive.
STATIC ELECTRICITY AND DISCHARGES
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charge at rest on the surface of an object. Why is it called static electricity? Because the charge stays in one place and then moves to another (ESD=Electro static discharge)
When this charge suddenly moves between 2 objects this is called electric discharge (shock)
What is lightning? Electric discharge traveling between a cloud and the ground or cloud to cloud.
How does lightning occur? Friction from wind blowing air, water, ice (Ice is positive) travels from the top of the rain cloud. (Water=negative) Water is on the bottom of the cloud. Wind charges the ground positively. A path is created to start lightning strike. Electrons are discharged in the path.
CHARGING BY CONTACT
There are two ways of depositing a charge on an object through contact:
-
Charging by friction
-
Charging by conduction
-
CHARGING BY FRICTION
When neutral objects made of different materials are rubbed together, electrons transfer from one object to another. The two object become charged. One object will gain electrons the other will lose electrons.
If the amount of friction is increase then the number of electrons being transferred increases.
How does humidity affect static electricity? When wet humid air collides with charged objects the water removes the charge by transferring electrons.
CHARGING BY CONDUCTION
A neutral object can become charged by direct contact with another object that is already charged. The electrons from one object move to the other with fewer electrons. The charge of both objects change.
CHARGING BY INDUCTION
Induced charge separation is a shift in the position of the electrons in a neutral object that occurs when a charged object is brought near it. Charging by induction refers to charging an object by bringing it close to, but not touching a charged object.
GROUNDING
You can neutralize any object by adding or removing electrons. When the object is connected to a large body such as earth the electric charge can be removed.
If a negative object is grounded then the electrons leave the object and travel into the ground until the object becomes neutral.
If a positive object is grounded the electrons leave the ground and travel into the object until the object becomes neutral.
Charging permanently by induction always produces an object with the opposite charge to the original charged object.
CHARGING AN OBJECT NEGATIVELY THROUGH CONDUCTION
-. Bring a negatively charged rod close to a neutral metal leaf electroscope
- the charged rod repels the e-s into the leaves causing the leaves to repel and spread apart
-the rod touches the sphere of the electroscope
-the negative rod transfers e-s to the electroscope
-the rod is removed
-the e-s spread out and the electroscope is now negatively charged
CHARGING AN OBJECT POSITIVELY THROUGH CONDUCTION
-. Bring a positively charged rod close to a neutral metal leaf electroscope
- the charged rod attracts the e-s into the sphere causing the leaves to repel and spread apart
-the rod touches the sphere of the electroscope
-the positive rod removes e-s from the electroscope
-the rod is removed
-the e-s spread out and the electroscope is now positively charged
CHARGING AN OBJECT NEGATIVELY THROUGH INDUCTION
- Bring a positively charged rod close to a neutral metal leaf electroscope
- The charged rod attracts the e-s into the head of the electroscope, causing the leaves to spread apart
- The groundwire touches the sphere of the electroscope
- The electrons from the ground transfer into the electroscope
- The groudwire is removed
- The rod is removed
- The electrons spread out and the electroscope is now negatively charged
CHARGING AN OBJECT POSITIVELY THROUGH INDUCTION
- Bring a negitively charged rod close to a neutral metal leaf electroscope
- The charged rod repels the e-s into the leaves of the electroscope, causing the leaves to spread apart
- The groundwire touches the sphere of the electroscope
- The electrons from the electroscope transfer into the ground
- The groudwire is removed
- The rod is removed
- The electrons spread out and the electroscope is now positively charged